Generate and Import Netlist
Generate Netlist
1. In Eeschema click on Generate netlist icon.
2. The netlist is generated.
The Layout of the Pcb
1. In KiCad (5.1.2) click on the PCB Layout Editor icon (i.e. the icon with gold PCB
board tracks).
2. A window opens with heading Pcbnew.
3. Click File and click Page settings.
4. A Page Settings window opens.
5. Fill in:
5.1 Revision: Version 01.
5.2 Title: Switching Regulator Controller LTC1624CS8.
5.3 Comment4: Your Name.
5.4 Click OK.
6. Click on Set units to inches icon, it is on the left, the icon with "in"
and an omnidirectional arrow below it.
7. Set Grid: 50,00 mils (1,2700mm) on the horizontal drop-down menu at the top.
Import Netlist
1. Click Tools and the Load Netlist … .
2. The Netlist window opens.
3. In the Netlist file: navigate to the TutorialName.net file.
4. Click Update PCB.
5. Click Close.
6. In PCB Layout Editor or Pcbnew, you should now see the footprint of the PCB and
thin white lines connecting the footprints.
7. The white lines are called a rat’s nest.
Minimum Design Rules:
OSHPARK1. Go to OSHPARK Fabrication Services
2. For a two-layer board their minimum design rules are shown in figure 1.13A below:

Fig. 1.13A: Oshpark Minimum Design Rules
3. Thus the minimum design rules as stated by OSHPARK are:
3.1. Trace clearance = 6 mil (0.1524mm).
3.2. Trace width = 6 mil (0.1524mm).
3.3. Drill size = 10 mil (0.254mm).
3.4. Annular ring = 5 mil (0.127mm).
Aisler
Minimum Design Rules
1. The minimum design rules as set out by Aisler are as shown in figure 1.13B below:
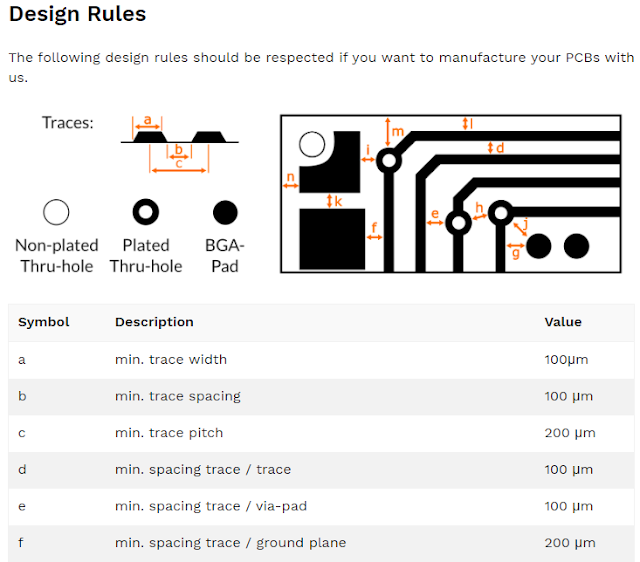
Fig 1.13B: Aisler Minimum Design Rules
2. Minimum trace width is 100um or 3.937mils say 4mils.
3. The minimum via diameter is 200um or 7.874mils or 8mil.
4. The minimum via diameter is 0.4mm or 16mil.
5. 300um = 11.811mils.
Trace, Track Clearance or Conductor Spacing and Vias
You can view this video on YouTube by clicking on: Trace, Track Clearance and Vias for PCB.
Trace, Track Clearance or Conductor Spacing
1. The IPC-2221A Generic Standard on Printed Board Design of May 2003 on
page 43 published the following table 6-1 regarding the minimum conductor spacing.
2. It is shown in figure 1.13C below:
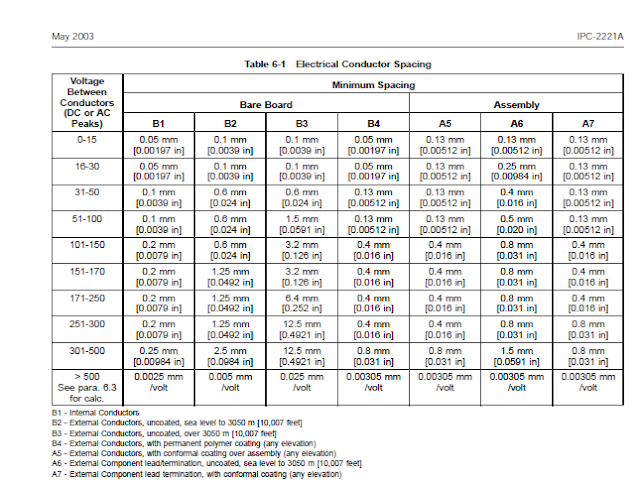
Fig. 1.13C: IPC-2221A Table 6-1 On Electrical Conductor Spacing
3. In figure 1.4B we saw that the highest peak voltage we measured was just below
18 volts.
4. So, if we choose Voltage Between Conductors (AC Peaks) in the second row
16-30 volts and in column A6 the Electrical Conductor Minimum Spacing is given
as 0.25 mm or 0.00984 in or 9.843 mils let say 10mils.
KiCad
1. This table is also available in KiCad itself.
2. Click on PCB Calculator and the on the Electrical Spacing tab.
3. You will see the following in figure 1.13D below:
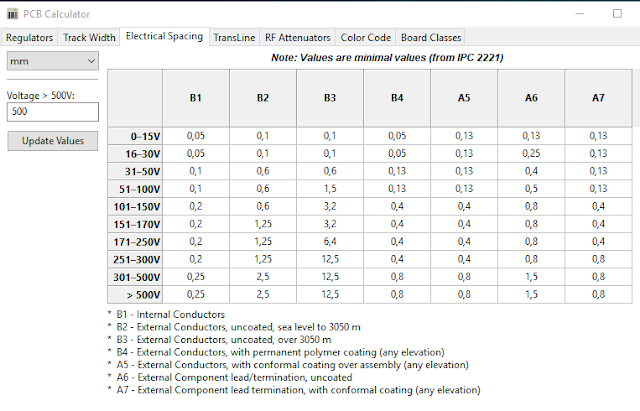
Fig. 1.13D: KiCad Electrical Spacing
4. In the 16-30V row and A6 column it is given as 0.25 mm, or 250 um or 9.843 mils.
Saturn PCB Design, PCB Toolkit V7.8
1. In the Saturn PCB Design, PCB Toolkit V7.8 click on the Conductor Spacing tab.
2. In the Minimum Conductor Spacing box and in Voltage Between Conductors
select 16 - 30.
3. In Device Type Selection select A6 – Assembly.
4. You should see the following in figure 1.13E:
 |
| Fig. 1.13E: Saturn PCB Conductor Spacing |
5. According to the Saturn PCB Design toolkit the minimum conductor spacing that
should be used is thus 0.25mm or 9.84mils.
6. This complies with the IPC-2221A Generic Standard on Printed Board Design
of May 2003.
7. This also complies with the Kicad PCB Calculator and the on the Electrical Spacing
8. The minimum trace clearance that can be manufactured by Oshpark is
0.1524mm or 6mil and can, therefore, manufacture the PCB.
9. The minimum spacing trace to trace that can be manufactured by Aisler is
100um or 0.100mm or 3.937mils and can, therefore, manufacture the PCB.
8. The minimum trace clearance that can be manufactured by Oshpark is
0.1524mm or 6mil and can, therefore, manufacture the PCB.
9. The minimum spacing trace to trace that can be manufactured by Aisler is
100um or 0.100mm or 3.937mils and can, therefore, manufacture the PCB.
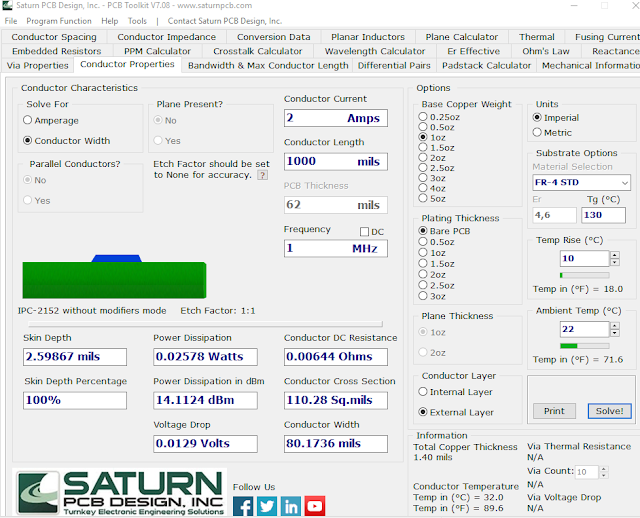
Vias
1. For the 2A conductor group in the Saturn PCB Design, toolkit select the
Via Properties tab.
2. Set
2.1 Layer Set = 2 Layer.
2.2 Temp Rise (C) = 10.
2.3 Via Height = 62 mils.
2.4 Via Plating Thickness 1 mils.
3. Now adjust Via Hole Diameter = 18 mils so that Via Current is equal to
approximately 2.00 Amps.
4. See the results in figure 1.13F below:
 |
| Fig. 1.13F: Saturn PCB Toolkit To Calculate Via |
5. For the 100mA conductor group in the Saturn PCB Design, toolkit select the
Via Properties tab.
6. Set:
6.1 Layer Set = 2 Layer.
6.2 Temp Rise (C) = 10.
6.3 Via Height = 62 mils.
6.4 Via Plating Thickness 1 mils.
7. We want to calculate the hole diameter for 100mA current.
8. Now if we adjust Via Hole Diameter = 5 mils so that Via Current is
equal to approximately 1.1795 Amps as shown in figure 1.13G below.
 |
| Fig. 1.13G: Via Diameter For 100mA Group |
0.254mm or 10 mil.
10. For Aisler for vias, the minimum via diameter is 0.2mm or 8mil and the
corresponding pad diameter should be at least 0.4mm or 16mil.
How Does The Solder Mask And Solder Mask Layer Work?
Solder Mask
1. Solder mask itself or solder stop mask or solder resist is a thin layer that is
applied to a printed circuit board or (PCB).
2. It is usually dark green or sometimes purple.
3. It is a physical substance applied to the printed circuit board.
4. There are holes in this mask or this layer that expose parts of the printed circuit board.
5. These holes in general expose the copper pads to which the components wire
are soldered.
6. These holes also expose parts of the printed circuit board itself.
Solder Mask Layer
1. The solder mask layer on the other hand is used to deposit the solder mask on the
printed circuit board.
2. It is said this solder mask layer is the negative of the solder mask.
3. A good explanation can found at:
4. As mentioned there are holes in the solder mask (physical layer on the printed
circuit board) that expose the printed circuit board.
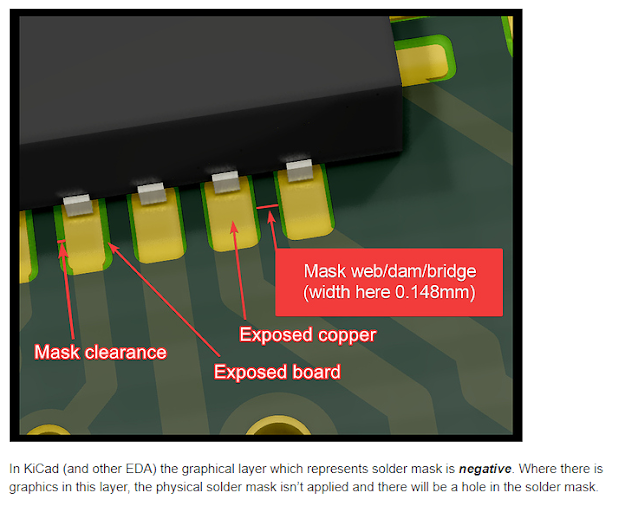
5. There are two very important parameters of a solder mask. They are:
5.1 solder mask clearance, and
5.2 solder mask minimum width.
6. This is shown in figure 1.13H below:
7. What is shown in figure 1.13H above as:
7.1 Mask clearance, is in fact, the solder mask clearance. It is the
distance between the edge of the mask and the edge of the copper pad.
7.2 Mask web/dam/bridge (width here 0.148mm), is in fact, the
solder mask minimum width. It is the minimum width that the solder mask
can be.
8. In KiCad the solder mask layer is represented by a graphical layer.
9. As mentioned this graphical solder mask layer of the solder mask is a negative
of the solder mask itself on the printed circuit board.
9
10. This means where there are graphics in the solder mask layer (something that
blocks the layer) the physical solder mask itself is not applied to the printed circuit board.
11. It also means where there are graphics there is an opening in the solder mask on
the printed circuit board and the printed circuit board is exposed.
12. The solder mask minimum width seen in fig. 1.13I the minimum width that can
be tolerated between the graphical items on the solder mask layer.
13. Shown in figure 1.13J below is shown what happens if the space between graphic
items is less that than the solder mask minimum width.
14. As can be seen, the too-thin parts between the graphic items are removed and
the area is merged in the Gerber files into a larger blob.
15. This solder mask layer minimum width has to do with the PCB manufacturer's
capability to create the required minimum width.
16. OSHPark has the following design rule setup for KiCad solder mask clearance shown
in figure 1.13K below:
17. The solder mask minimum width given by OSHPark is described as the
minimum soldermask web and is given as 4 mil (0.1016mm) as shown in figure 1.13L below.
 |
| Fig. 1.13L: OSHPark Solder Mask Minimum Width |
18. The minimum recommendations by OSHPark are, therefore:
18.1 Solder mask clearance = 0.0508mm or 0.002in or 2mils.
18.2 Solder mask minimum width = 0.101mm or 0.004in or 4mils.
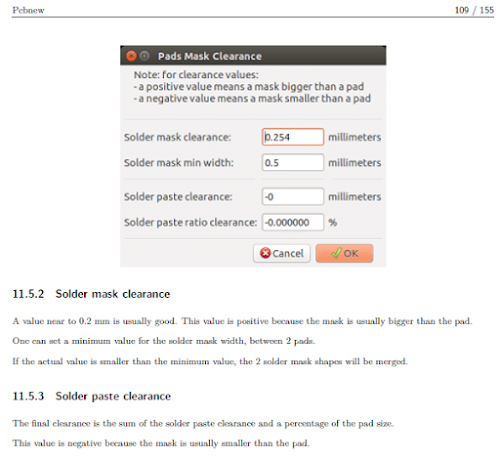
19. The recommendation in KiCad Pcbnew of May 25, 2020, is given in
figure 1.13M below:
1. The solder mask also called solder resist is used to stop solder from forming on
the traces.
2. In general, a solder mask opening is set so that it is 4mils larger than the
copper pad it is exposing or the opening is 2mils larger on each side.
Setup Design Rules
2. The Board Setup window opens.
3. Follow the recommendations of the PCB manufacturer.
"Global Design Rules tab".
5. Under Design Rules click on Solder Mask/Paste
6. Set:
6.1. Solder mask clearance: 2 mils.
6.2. Solder mask minimum width: 4 mils.
6.3. Click OK.
7. See figure 1.13H below:
 |
| Fig. 1.13G: Solder Mask Clearance and Width |
8. In Pcbnew click File click Board Setup… .
9. Board Setup window opens.
10. Click on Design Rules.
11. Leave Allow blind/buried vias unchecked.
12. Leave Allow micro vias (uVias) unchecked.
13. Set Minimum track width: 6,0 mils (Oshpark).
14. Set Minimum via diameter: 20,0 mils (Use Oshpark minimum drill at 10,0mils
and double it).
15. Set Minimum via drill: 10,0 mils (Use Oshpark minimum drill at 10,0mils).
16. Set Minimum uVia diameter: 20,0 mils.
17. Set Minimum uVia drill: 10,0 mils.
radii if 2 different drills are used)
19. See figure 1.13I below for design rules setup:
1. In the Board Setup window and under Design Rules click on Net Classes.
2. In general, you must try and make your tracks a bit wider than the minimum width.
3. Set:
3.1. Name: Default
3.2. Clearance: 10 mils.
3.3. Track Width: 10 mils.
3.4. Via Size: 30 mils.
3.5. Via Drill: 15 mils.
3.6. uVia Size: 30 mils.
3.7. uVia Drill: 15 mils.
2. Set:
2.1. Name: Signal
2.2. Clearance: 10 mils. (as discussed above)
2.3. Track Width: 10 mils. (as discussed in tutorial 1.12 Trace or Conductor
Width Calculation for PCB a conductor width of 4 mils can conduct
0.3378A. However, the minimum trace width of Oshpark is 6mils
but let's make it 10mils ).
2.4. Via Size: 20 mils. (Based on via drill = 10mil x 2 = 20mil).
2.5. Via Drill: 10 mils. (Oshpark minimum drill size that can be manufactured
is 10mil).
2.6. uVia Size: 20 mils.
2.7. uVia Drill: 10 mils.
 |
| Fig. 1.13I: Design Rules Setup |
Net Classes
Default
1. In the Board Setup window and under Design Rules click on Net Classes.
2. In general, you must try and make your tracks a bit wider than the minimum width.
3. Set:
3.1. Name: Default
3.2. Clearance: 10 mils.
3.3. Track Width: 10 mils.
3.4. Via Size: 30 mils.
3.5. Via Drill: 15 mils.
3.6. uVia Size: 30 mils.
3.7. uVia Drill: 15 mils.
Below 100mA Current Group signal
S
1. For maximum current of 100mA.2. Set:
2.1. Name: Signal
2.3. Track Width: 10 mils. (as discussed in tutorial 1.12 Trace or Conductor
Width Calculation for PCB a conductor width of 4 mils can conduct
0.3378A. However, the minimum trace width of Oshpark is 6mils
but let's make it 10mils ).
2.4. Via Size: 20 mils. (Based on via drill = 10mil x 2 = 20mil).
2.5. Via Drill: 10 mils. (Oshpark minimum drill size that can be manufactured
is 10mil).
2.6. uVia Size: 20 mils.
2.7. uVia Drill: 10 mils.
Below 2A Current Group
Power
1. For a Maximum Current of 2A
2. Set
2.1. Name: Power
2.2. Clearance: 10 mils. (as discussed above)
2.3. Track Width: 22 mils. (as discussed in tutorial 1.12 Trace or Conductor
Width Calculation for PCB ).
2.4. Via Size: 36 mils. (Based on via drill = 18mil x 2 = 36mil).
2.5. Via Drill: 18 mils. (As calculated above.)
2.6. uVia Size: 36 mils.
2.7. uVia Drill: 18 mils.
5. In the end, the net classes should be as in figure 1.13J below:
Net Class: Signal (Below 100mA)
2. Set
2.1. Name: Power
2.2. Clearance: 10 mils. (as discussed above)
2.3. Track Width: 22 mils. (as discussed in tutorial 1.12 Trace or Conductor
Width Calculation for PCB ).
2.4. Via Size: 36 mils. (Based on via drill = 18mil x 2 = 36mil).
2.5. Via Drill: 18 mils. (As calculated above.)
2.6. uVia Size: 36 mils.
2.7. uVia Drill: 18 mils.
3. dPair stands for differential pair.
4. We do not have a differential pair I this circuit thus we do have to concern us with
dPair.
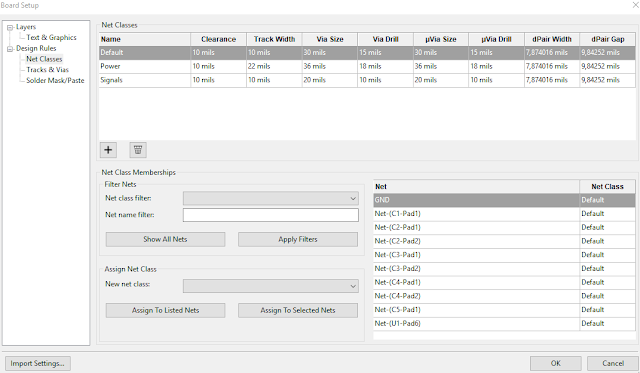 |
| Fig. 1.13J: Net Classes |
Net Class: Signal (Below 100mA)
1. By studying the circuit diagram the only track that can safely said to fall in the signal class
is the track in which capacitor C3 appears.
2. It is described in the net having capacitor C3 pad 1 and the net having capacitor C3 pad 2.
3. These two tracks should therefore be allocated to the net class Signal.
4. Net Class Signal and the two nets allocated to the class is shown in figure 1.13K below:
Fig. 1.13K: Net Class Signal With Two Nets C3-Pad1 and C3-Pad2
Net Class: Power (Below 2A)
1. The rest of the tracks are classified to fall in the below 2A category.
2. While it is true that there are other tracks that also fall in the below 100mA category this
approach is the safest especially if you build the circuit for the first time.
3. Net Class Power and the nets allocated to the class is shown in figure 1.13L below:
Tracks and Vias
1. Select Tracks & Vias
2. Under Tracks Width type 22 mils and 10 mils.
3. Under Vias Size type 36 mils and 20 mils.
4. Under Vias Drill type 18 mils and 10 mils.
2. Under Tracks Width type 22 mils and 10 mils.
3. Under Vias Size type 36 mils and 20 mils.
4. Under Vias Drill type 18 mils and 10 mils.
5. It should look like figure 1.13K below:
Previous: Tutorial 1.12: Trace, Track or Conductor Width Calculation for PCB
Next: Tutorial 1.14: Place Footprints, Draw Board, Route Tracks
 |
| Fig. 1.13K: Track Width Via Size and Drill. |
Previous: Tutorial 1.12: Trace, Track or Conductor Width Calculation for PCB
Next: Tutorial 1.14: Place Footprints, Draw Board, Route Tracks